Search Results for: lactic acid
Lactic acid
Definition noun (1) A colorless or yellowish, syrupy, water-soluble liquid, which is a byproduct of anaerobic glucose... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Lactate level
Definition noun A measure of the amount of lactic acid in the blood. Supplement The acid form of lactate (lactic acid) is... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
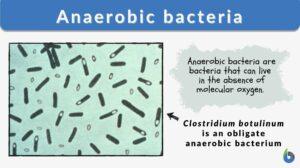
Anaerobic bacteria
Bacteria are classified according to the need for oxygen to survive and grow. For example, aerobic bacteria are bacteria... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Lactobacillus casei
Definition noun A non-pathogenic and harmless bacterium recognized widely as probiotics that controls growth of various... Read More
Cell Respiration
As mentioned in the previous tutorial on ATP, the process of respiration is split into 3 distinct areas that occur at... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Metabolite
Definition noun, plural: metabolites A substance that is a product of metabolic action or that is involved in a metabolic... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Guanosine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: guanosine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide made up of guanine, ribose, and two phosphate... Read More
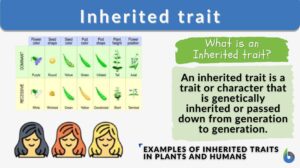
Inherited traits
What are Inherited Traits? The characteristics or traits that are passed from parents to offspring are known as inherited... Read More
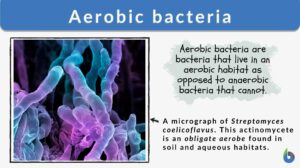
Aerobic bacteria
Aerobic Bacteria Definition What does aerobic mean in biology? As the name suggests, 'aerobe' in biology means organisms... Read More
Ferrous lactate
Definition noun A greenish white crystal or (powder) made up of iron (Fe2+) and lactate anions Supplement Ferrous lactate is... Read More
Streptococcus
Definition noun, plural: streptococci (1) A genus of bacteria characterized by being coccus, Gram-positive, and occurring in... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Aerotolerant
Aerotolerant Definition The term "aerotolerant" pertains to an organism that does not require oxygen for growth but can... Read More
Muscle fatigue
Definition noun (physiology) A condition of the muscle in which its capacity to produce maximum voluntary action, or to... Read More
Enterobacteriaceae
Definition noun: (taxonomy) A family of gram-negative bacilli that inhabit the large intestine of humans and other... Read More
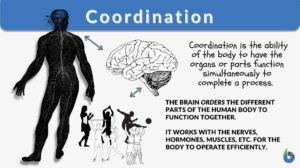
Coordination
Coordination Definition When a person hears the word coordination, they think of order, organization, or even managing... Read More
Doderleins bacillus
Doderlein's bacillus is a large, Gram-positive bacterium found in vaginal secretions. It is named after the German... Read More
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More